Lab 12: Lymphatic & Respiratory systems
When you are prepared for the Test on Week 12 Learning Objectives in Week 13, you will be able to:
- Identify major lymphatic organs and describe their functions.
- Identify regional collections of lymph nodes in the body and structures associated with individual lymph nodes.
- Identify structures of the upper respiratory tract and describe their functions.
- Identify structures of the larynx and lower respiratory tract and describe their functions.
- Identify important tissues of the respiratory system and which functions they perform.
- Describe the pathway that air travels through the body during inhalation and exhalation.
In Week 12, we will study two organ systems, the lymphatic and respiratory systems, that both work closely with the cardiovascular system to carry out important functions in the body.
The Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system includes organs and vessels dispersed throughout the body that assist in two major functions: returning excess fluid from tissues to the bloodstream and monitoring body fluids for pathogens in order to mount an immune response. Lymphatic vessels absorb and return interstitial fluid to the vessels of the circulatory system. They also transport lymphocytes, the main cells of the immune system. Lymphocytes come from the hematopoietic system of the bone marrow. Primary lymphoid organs, the bone marrow and thymus gland, are the locations where lymphocytes proliferate and mature. Secondary lymphoid organs are the site in which mature lymphocytes congregate to mount immune responses. Many immune system cells use the lymphatic and circulatory systems for transport throughout the body to search for and then protect against pathogens.
Functions of the Lymphatic System
A major function of the lymphatic system is to drain body fluids and return them to the bloodstream. Blood pressure causes leakage of fluid from the capillaries, resulting in the accumulation of fluid in the interstitial space—that is, spaces between individual cells in the tissues. In humans, 20 liters of plasma is released into the interstitial space of the tissues each day due to capillary filtration. Once this filtrate is out of the bloodstream and in the tissue spaces, it is referred to as interstitial fluid. Of this, 17 liters is reabsorbed directly by the blood vessels. But what happens to the remaining three liters? This is where the lymphatic system comes into play. It drains the excess fluid and empties it back into the bloodstream via a series of vessels, trunks, and ducts. Lymph is the term used to describe interstitial fluid once it has entered the lymphatic system. When the lymphatic system is damaged in some way, such as by being blocked by cancer cells or destroyed by injury, protein-rich interstitial fluid accumulates (sometimes “backs up” from the lymph vessels) in the tissue spaces. This inappropriate accumulation of fluid referred to as lymphedema may lead to serious medical consequences.
As the vertebrate immune system evolved, the network of lymphatic vessels became convenient avenues for transporting the cells of the immune system. Additionally, the transport of dietary lipids and fat-soluble vitamins absorbed in the gut uses this system.
Cells of the immune system not only use lymphatic vessels to make their way from interstitial spaces back into the circulation, but they also use lymph nodes as major staging areas for the development of critical immune responses. A lymph node is one of the small, bean-shaped organs located throughout the lymphatic system.
Structure of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic vessels begin as a blind ending, or closed at one end, capillaries, which feed into larger and larger lymphatic vessels, and eventually empty into the bloodstream by a series of ducts. Along the way, the lymph travels through the lymph nodes, which are commonly found near the groin, armpits, neck, chest, and abdomen. Humans have about 500–600 lymph nodes throughout the body (Figure 12.1).
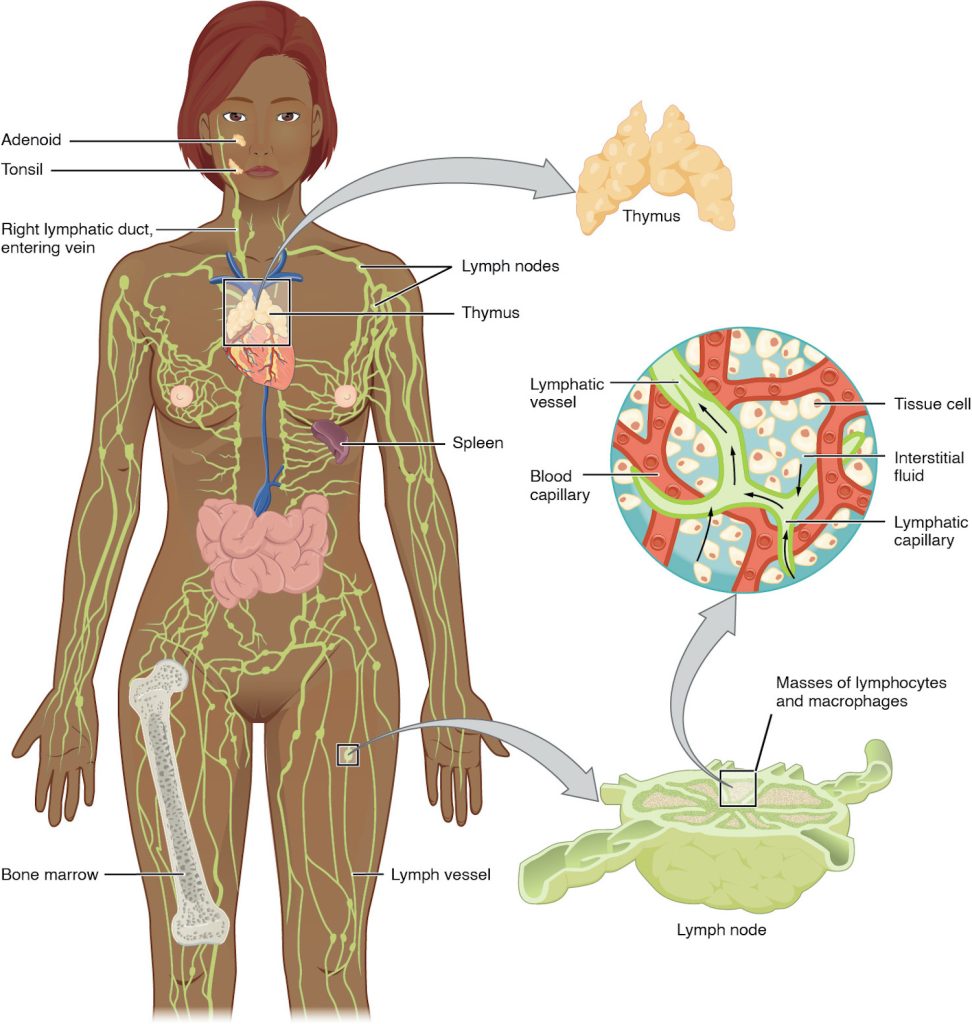
A major distinction between the lymphatic and cardiovascular systems in humans is that lymph is not actively pumped by the heart, but is forced through the vessels by the movements of the body, the contraction of skeletal muscles during body movements, and breathing. One-way valves (semi-lunar valves) in lymphatic vessels keep the lymph moving toward the heart. Lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the circulatory system via the lymphatic ducts located at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins in the neck.
Lymphatic Capillaries
Lymphatic capillaries, also called the terminal lymphatics, are vessels where interstitial fluid enters the lymphatic system to become lymph fluid. Located in almost every tissue in the body, these vessels are interlaced among the arterioles and venules of the circulatory system in the soft connective tissues of the body (Figure 12.2). Exceptions are the central nervous system, bone marrow, bones, teeth, and the cornea of the eye, which do not contain lymph vessels.

Lymphatic capillaries are formed by a one cell-thick layer of endothelial cells and represent the open end of the system, allowing interstitial fluid to flow into them via overlapping cells (see Figure 12.2). When interstitial pressure is low, the endothelial flaps close to prevent “backflow.” As interstitial pressure increases, the spaces between the cells open up, allowing the fluid to enter. Entry of fluid into lymphatic capillaries is also enabled by the collagen filaments that anchor the capillaries to surrounding structures. As interstitial pressure increases, the filaments pull on the endothelial cell flaps, opening up them even further to allow easy entry of fluid.
In the small intestine, lymphatic capillaries called lacteals are critical for the transport of dietary lipids and lipid-soluble vitamins to the bloodstream. In the small intestine, dietary triglycerides combine with other lipids and proteins, and enter the lacteals to form a milky fluid called chyle. The chyle then travels through the lymphatic system, eventually entering the bloodstream.
Larger Lymphatic Vessels, Trunks, and Ducts
The lymphatic capillaries empty into larger lymphatic vessels, which are similar to veins in terms of their three-tunic structure and the presence of valves. These one-way valves are located fairly close to one another, and each one causes a bulge in the lymphatic vessel, giving the vessels a beaded appearance.
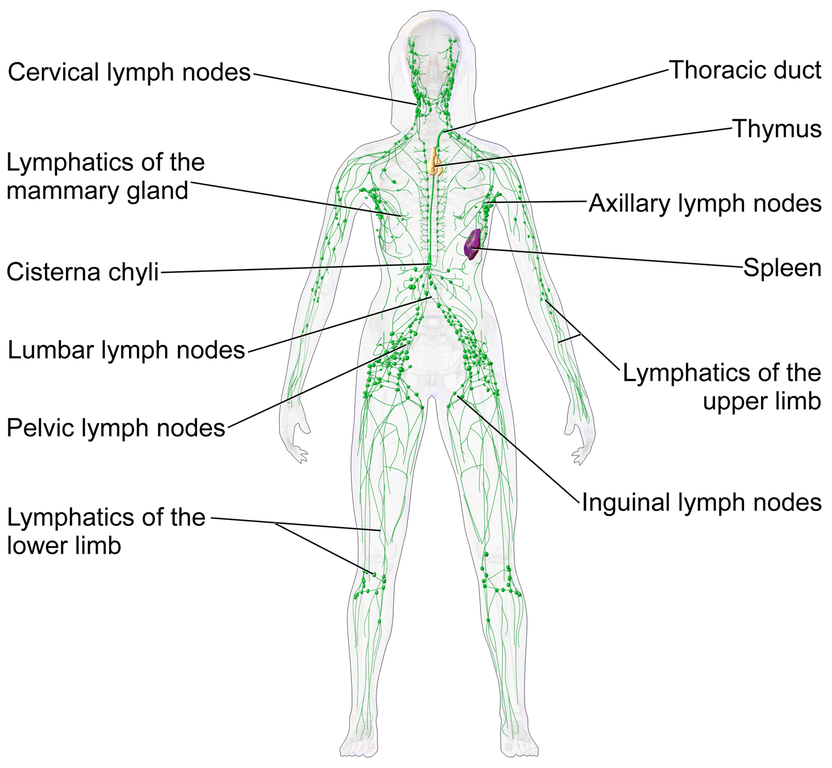
The superficial and deep lymphatics eventually merge to form larger lymphatic vessels known as lymphatic trunks. On the right side of the body, the right sides of the head, thorax, and right upper limb drain lymph fluid into the right subclavian vein via the right lymphatic duct. On the left side of the body, the remaining portions of the body drain into the larger thoracic duct, which drains into the left subclavian vein. The thoracic duct itself begins just beneath the diaphragm in the cisterna chyli, a sac-like chamber that receives lymph from the lower abdomen, pelvis, and lower limbs by way of the left and right lumbar trunks and the intestinal trunk (Figure 12.3)

The overall drainage system of the body is asymmetrical. The right lymphatic duct receives lymph from only the upper right side of the body. The lymph from the rest of the body enters the bloodstream through the thoracic duct via all the remaining lymphatic trunks. In general, lymphatic vessels of the subcutaneous tissues of the skin, that is, the superficial lymphatics, follow the same routes as veins, whereas the deep lymphatic vessels of the viscera generally follow the paths of arteries.
Primary Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Development
Understanding the differentiation and development of B and T cells is critical to the understanding of the adaptive immune response. It is through this process that the body (ideally) learns to destroy only pathogens and leaves the body’s own cells relatively intact. The primary lymphoid organs are the bone marrow and thymus gland. The primary lymphoid organs are where lymphocytes mature, proliferate, and are selected, which enables them to attack pathogens without harming the cells of the body.
Bone Marrow
In the embryo, blood cells are made in the yolk sac. As development proceeds, this function is taken over by the spleen, lymph nodes, and liver. Later, the bone marrow takes over most hematopoietic functions, although the final stages of the differentiation of some cells may take place in other organs. The red bone marrow is a loose collection of cells where hematopoiesis occurs (review Chapters 4 and 10 for the location of red bone marrow and a discussion on hematopoiesis, respectively). The B cell undergoes nearly all of its development in the red bone marrow, whereas the immature T cell, called a thymocyte, leaves the bone marrow and matures largely in the thymus gland.
Thymus
The thymus gland is a bilobed organ found in the space between the sternum and the aorta of the heart (Figure 12.4). It is larger and more active during infancy and early childhood, and begins to atrophy as we age.
Connective tissue holds the lobes closely together but also separates them and forms a capsule. The connective tissue capsule further divides the thymus into lobules via extensions called trabeculae. The outer region of the organ is known as the cortex and contains large numbers of thymocytes with some epithelial cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells (two types of phagocytic cells that are derived from monocytes). The cortex is densely packed so it stains more intensely than the rest of the thymus. The medulla, where thymocytes migrate before leaving the thymus, contains a less dense collection of thymocytes, epithelial cells, and dendritic cells.

Secondary Lymphoid Organs and their Roles in Active Immune Responses
Lymphocytes develop and mature in the primary lymphoid organs, but they mount immune responses from the secondary lymphoid organs. A naïve lymphocyte is one that has left the primary organ and entered a secondary lymphoid organ. Naïve lymphocytes are fully functional immunologically, but have yet to encounter an antigen to respond to. In addition to circulating in the blood and lymph, lymphocytes concentrate in secondary lymphoid organs, which include the lymph nodes, spleen, and lymphoid nodules. All of these tissues have many features in common, including the following:
- The presence of lymphoid follicles, the sites of the formation of lymphocytes, with specific B cell-rich and T cell-rich areas
- An internal structure of reticular fibers with associated fixed macrophages
- Germinal centers, which are the sites of rapidly dividing B lymphocytes and plasma cells, with the exception of the spleen
- Specialized post-capillary vessels known as high endothelial venules; the cells lining these venules are thicker and more columnar than normal endothelial cells, which allow cells from the blood to directly enter these tissues
Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are found in many areas of the body and are often located in clusters that lymph vessels connect to and flow through. Figure 12.5 shows the locations of lymph nodes throughout the body.
Lymph nodes function to remove debris and pathogens from the lymph, and are thus sometimes referred to as the “filters of the lymph” (Figure 12.6). Any bacteria that infect the interstitial fluid are taken up by the lymphatic capillaries and transported to a regional lymph node. Dendritic cells and macrophages within this organ internalize and kill many of the pathogens that pass through, thereby removing them from the body. The lymph node is also the site of adaptive immune responses mediated by T cells, B cells, and accessory cells of the adaptive immune system. Like the thymus, the bean-shaped lymph nodes are surrounded by a tough capsule of connective tissue and are separated into compartments by trabeculae, the extensions of the capsule. In addition to the structure provided by the capsule and trabeculae, the structural support of the lymph node is provided by a series of reticular fibers laid down by fibroblasts.

The major routes into the lymph node are via afferent lymphatic vessels (Figure 12.6). Cells and lymph fluid that leave the lymph node may do so by another set of vessels known as the efferent lymphatic vessels. Lymph enters the lymph node via the subcapsular sinus, which is occupied by dendritic cells, macrophages, and reticular fibers. Within the cortex of the lymph node are lymphoid follicles, which consist of germinal centers of rapidly dividing B cells surrounded by a layer of T cells and other accessory cells. As the lymph continues to flow through the node, it enters the medulla, which consists of medullary cords of B cells and plasma cells, and the medullary sinuses where the lymph collects before leaving the node via the efferent lymphatic vessels.
Spleen
In addition to the lymph nodes, the spleen is a major secondary lymphoid organ (Figure 12.7). It is about 12 cm (5 in) long and is attached to the lateral border of the stomach via the gastrosplenic ligament. The spleen is a fragile organ without a strong capsule, and is dark red due to its extensive vascularization. The spleen is sometimes called the “filter of the blood” because of its extensive vascularization and the presence of macrophages and dendritic cells that remove microbes and other materials from the blood, including dying red blood cells. The spleen also functions as the location of immune responses to blood-borne pathogens.

The spleen is also divided by trabeculae of connective tissue, and within each splenic nodule is an area of red pulp, consisting of mostly red blood cells, and white pulp, which resembles the lymphoid follicles of the lymph nodes. Upon entering the spleen, the splenic artery splits into several arterioles (surrounded by white pulp) and eventually into sinusoids. Blood from the capillaries subsequently collects in the venous sinuses and leaves via the splenic vein. The red pulp consists of reticular fibers with fixed macrophages attached, free macrophages, and all of the other cells typical of the blood, including some lymphocytes. The white pulp surrounds a central arteriole and consists of germinal centers of dividing B cells surrounded by T cells and accessory cells, including macrophages and dendritic cells. Thus, the red pulp primarily functions as a filtration system of the blood, using cells of the relatively nonspecific immune response, and white pulp is where adaptive T and B cell responses are mounted.
Lymphoid Nodules
The other lymphoid tissues, the lymphoid nodules, have a simpler architecture than the spleen and lymph nodes in that they consist of a dense cluster of lymphocytes without a surrounding fibrous capsule. These nodules are located in the respiratory and digestive tracts, areas routinely exposed to environmental pathogens.
Tonsils are lymphoid nodules located along the inner surface of the pharynx and are important in developing immunity to oral pathogens (Figure 12.8). The tonsil located at the back of the throat, the pharyngeal tonsil, is sometimes referred to as the adenoid when swollen. Such swelling is an indication of an active immune response to infection. Histologically, tonsils do not contain a complete capsule, and the epithelial layer invaginates deeply into the interior of the tonsil to form tonsillar crypts. These structures, which accumulate all sorts of materials taken into the body through eating and breathing, actually “encourage” pathogens to penetrate deep into the tonsillar tissues where they are acted upon by numerous lymphoid follicles and eliminated. This seems to be the major function of tonsils—to help children’s bodies recognize, destroy, and develop immunity to common environmental pathogens so that they will be protected in their later lives. Tonsils are often removed in those children who have recurring throat infections, especially those involving the palatine tonsils on either side of the throat, whose swelling may interfere with their breathing and/or swallowing.

Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) consists of an aggregate of lymphoid follicles directly associated with the mucous membrane epithelia. MALT makes up dome-shaped structures found underlying the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract, breast tissue, lungs, and eyes. Peyer’s patches, a type of MALT in the small intestine, are especially important for immune responses against ingested substances (Figure 12.9). Peyer’s patches contain specialized endothelial cells called M (or microfold) cells that sample material from the intestinal lumen and transport it to nearby follicles so that adaptive immune responses to potential pathogens can be mounted.

Bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) consists of lymphoid follicular structures with an overlying epithelial layer found along the bifurcations of the bronchi, and between bronchi and arteries. They also have the typically less-organized structure of other lymphoid nodules. These tissues, in addition to the tonsils, are effective against inhaled pathogens.
The Respiratory System
Hold your breath. Really! See how long you can hold your breath as you continue reading…How long can you do it? Chances are you are feeling uncomfortable already. A typical human cannot survive without breathing for more than 3 minutes, and even if you wanted to hold your breath longer, your autonomic nervous system would take control. This is because every cell in the body needs to run the oxidative stages of cellular respiration, the process by which energy is produced in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). For oxidative phosphorylation to occur, oxygen is used as a reactant and carbon dioxide is released as a waste product. Carbon dioxide is exhaled and oxygen is inhaled through the respiratory system, which includes muscles to move air into and out of the lungs, passageways through which air moves, and microscopic gas exchange surfaces covered by capillaries. The circulatory system transports gases from the lungs to tissues throughout the body and vice versa.
Organs and Structures of the Respiratory system
The major organs of the respiratory system function primarily to provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration, remove the waste product carbon dioxide, and help to maintain acid-base balance (Figure 12.10). Portions of the respiratory system are also used for non-vital functions, such as sensing odors, speech production, and for straining, such as during childbirth or coughing.

Functionally, the respiratory system can be divided into a conducting zone and a respiratory zone. The conducting zone of the respiratory system includes the organs and structures not directly involved in gas exchange. The gas exchange occurs in the respiratory zone.
Conducting Zone
The major functions of the conducting zone are to provide a route for incoming and outgoing air, remove debris and pathogens from the incoming air, and warm and humidify the incoming air. Several structures within the conducting zone perform other functions as well. The epithelium of the nasal passages, for example, is essential to sensing odors, and the bronchial epithelium that lines the lungs can metabolize some airborne carcinogens.
The Nose and its Adjacent Structures
The major entrance and exit for the respiratory system is through the nose. Underneath the thin skin of the nose are its skeletal features. While the root and bridge of the nose consist of bone, the protruding portion of the nose is composed of cartilage. As a result, when looking at a skull, the nose is missing. The nasal bone is one of a pair of bones that lies under the root and bridge of the nose. The nasal bone articulates superiorly with the frontal bone and laterally with the maxillary bones. Septal cartilage is flexible hyaline cartilage connected to the nasal bone, forming the dorsum nasi. The alar cartilage consists of the apex of the nose; it surrounds the naris.
The nares open into the nasal cavity, which is separated into left and right sections by the nasal septum. The nasal septum is formed anteriorly by a portion of the septal cartilage (the flexible portion you can touch with your fingers) and posteriorly by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone (a cranial bone located just posterior to the nasal bones) and the thin vomer bone (whose name refers to its plough shape). Each lateral wall of the nasal cavity has three bony projections, called the superior, middle, and inferior nasal conchae. The inferior conchae are separate bones, whereas the superior and middle conchae are portions of the ethmoid bone. Conchae serve to increase the surface area of the nasal cavity and to disrupt the flow of air as it enters the nose, causing air to bounce along the epithelium, where it is cleaned and warmed. The conchae and meatuses also conserve water and prevent dehydration of the nasal epithelium by trapping water during exhalation. The floor of the nasal cavity is composed of the palate. The hard palate at the anterior region of the nasal cavity is composed of bone. The soft palate at the posterior portion of the nasal cavity consists of muscle tissue. Air exits the nasal cavities via the internal nares and moves into the pharynx (Figure 12.11).

Several bones that help form the walls of the nasal cavity have air-containing spaces called the paranasal sinuses, which serve to warm and humidify incoming air. Sinuses are lined with a mucosa. Each paranasal sinus is named for its associated bone: frontal sinus, maxillary sinus, sphenoidal sinus, and ethmoidal sinus. The sinuses produce mucus and lighten the weight of the skull.
The nares and anterior portion of the nasal cavities are lined with mucous membranes, containing sebaceous glands and hair follicles that serve to prevent the passage of large debris, such as dirt, through the nasal cavity. An olfactory epithelium used to detect odors is found deeper in the nasal cavity.
The conchae, meatuses, and paranasal sinuses are lined by respiratory epithelium composed of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (Figure 12.12). The epithelium contains goblet cells, one of the specialized, columnar epithelial cells that produce mucus to trap debris. The cilia of the respiratory epithelium help remove the mucus and debris from the nasal cavity with a constant beating motion, sweeping materials towards the throat to be swallowed. Interestingly, cold air slows the movement of the cilia, resulting in accumulation of mucus that may in turn lead to a runny nose during cold weather. This moist epithelium functions to warm and humidify incoming air. Capillaries located just beneath the nasal epithelium warm the air by convection. Serous and mucus-producing cells also secrete the lysozyme enzyme and proteins called defensins, which have antibacterial properties. Immune cells that patrol the connective tissue deep to the respiratory epithelium provide additional protection.

Pharynx
The pharynx is a tube formed by skeletal muscle and lined by mucous membrane that is continuous with that of the nasal cavities (Figure #). The pharynx is divided into three major regions: the nasopharynx, the oropharynx, and the laryngopharynx (Figure 12.13).
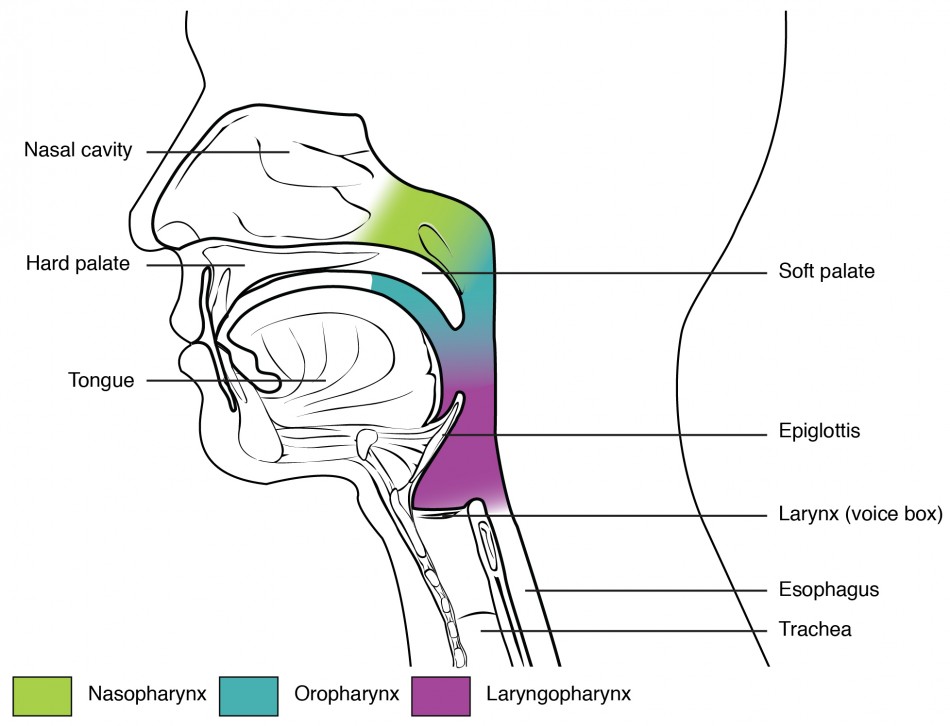
The nasopharynx is flanked by the conchae of the nasal cavity, and it serves only as an airway. At the top of the nasopharynx are the pharyngeal tonsils. A pharyngeal tonsil, also called an adenoid, is an aggregate of lymphoid reticular tissue similar to a lymph node that lies at the superior portion of the nasopharynx. The function of the pharyngeal tonsil is not well understood, but it contains a rich supply of lymphocytes and is covered with ciliated epithelium that traps and destroys invading pathogens that enter during inhalation. The pharyngeal tonsils are large in children, but interestingly, tend to regress with age and may even disappear. The uvula is a small bulbous, teardrop-shaped structure located at the apex of the soft palate. Both the uvula and soft palate move like a pendulum during swallowing, swinging upward to close off the nasopharynx to prevent ingested materials from entering the nasal cavity. In addition, auditory (Eustachian) tubes that connect to each middle ear cavity open into the nasopharynx. This connection is why colds often lead to ear infections.
The oropharynx is a passageway for both air and food. The oropharynx is bordered superiorly by the nasopharynx and anteriorly by the oral cavity. The fauces is the opening at the connection between the oral cavity and the oropharynx. As the nasopharynx becomes the oropharynx, the epithelium changes from pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium to stratified squamous epithelium. The oropharynx contains two distinct sets of tonsils, the palatine and lingual tonsils. A palatine tonsil is one of a pair of structures located laterally in the oropharynx in the area of the fauces. The lingual tonsil is located at the base of the tongue. Similar to the pharyngeal tonsil, the palatine and lingual tonsils are composed of lymphoid tissue, and trap and destroy pathogens entering the body through the oral or nasal cavities.
The laryngopharynx is inferior to the oropharynx and posterior to the larynx. It continues the route for ingested material and air until its inferior end, where the digestive and respiratory systems diverge. The stratified squamous epithelium of the oropharynx is continuous with the laryngopharynx. Anteriorly, the laryngopharynx opens into the larynx, whereas posteriorly, it enters the esophagus.
Larynx
The larynx is a cartilaginous structure inferior to the laryngopharynx that connects the pharynx to the trachea and helps regulate the volume of air that enters and leaves the lungs (Figure 12.14). The structure of the larynx is formed by several pieces of cartilage. Three large cartilage pieces—the thyroid cartilage (anterior), epiglottis (superior), and cricoid cartilage (inferior)—form the major structure of the larynx. The thyroid cartilage is the largest piece of cartilage that makes up the larynx. The thyroid cartilage consists of the laryngeal prominence, or “Adam’s apple,” which tends to be more prominent in males. The thick cricoid cartilage forms a ring, with a wide posterior region and a thinner anterior region. Three smaller, paired cartilages—the arytenoids, corniculates, and cuneiforms—attach to the epiglottis and the vocal cords and muscle that help move the vocal cords to produce speech.
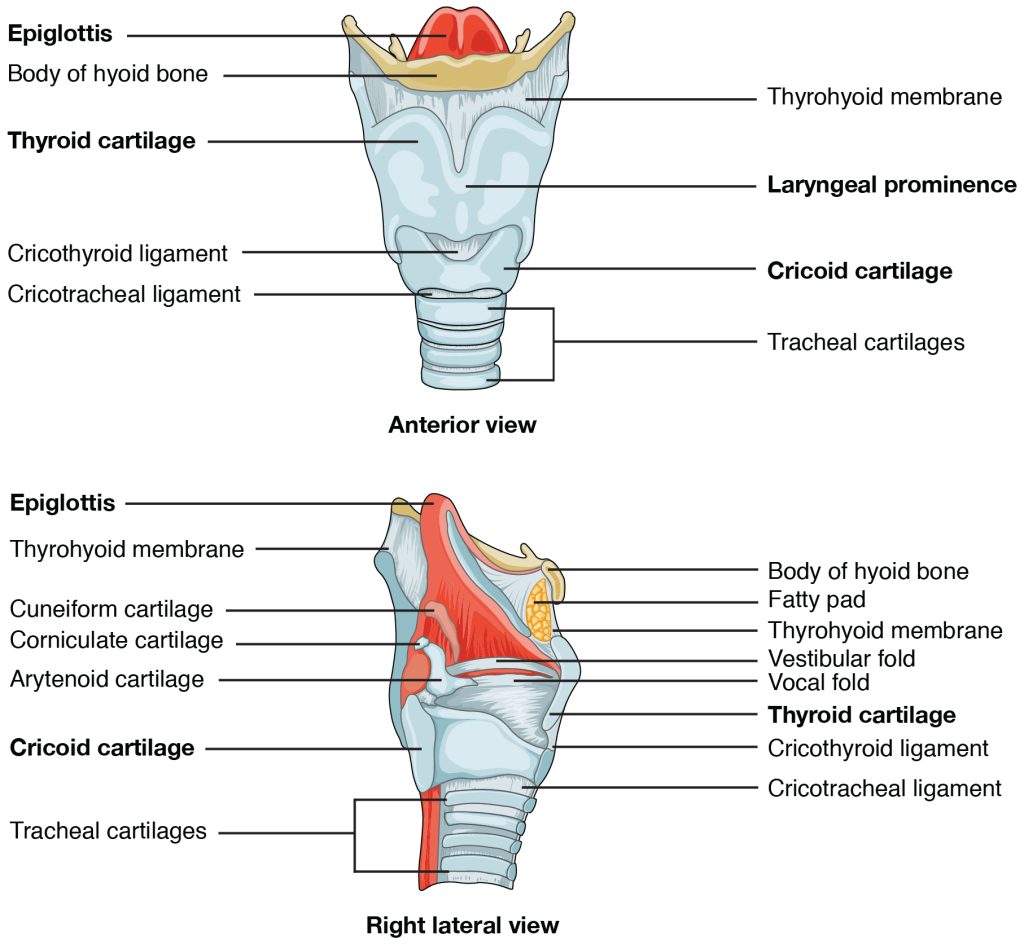
The epiglottis, attached to the thyroid cartilage, is a very flexible piece of elastic cartilage that covers the opening of the trachea. When in the “closed” position, the unattached end of the epiglottis rests on the glottis. The glottis is composed of the vestibular folds, the true vocal cords, and the space between these folds (Figure 12.15). A vestibular fold, or false vocal cord, is one of a pair of folded sections of mucous membrane. A true vocal cord is one of the white, membranous folds attached by muscle to the thyroid and arytenoid cartilages of the larynx on their outer edges. The inner edges of the true vocal cords are free, allowing oscillation to produce sound. The size of the membranous folds of the true vocal cords differs between individuals, producing voices with different pitch ranges. Folds in males tend to be larger than those in females, which create a deeper voice. The act of swallowing causes the pharynx and larynx to lift upward, allowing the pharynx to expand and the epiglottis of the larynx to swing downward, closing the opening to the trachea. These movements produce a larger area for food to pass through, while preventing food and beverages from entering the trachea.

Continuous with the laryngopharynx, the superior portion of the larynx is lined with stratified squamous epithelium, transitioning into pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium that contains goblet cells. Similar to the nasal cavity and nasopharynx, this specialized epithelium produces mucus to trap debris and pathogens as they enter the trachea. The cilia beat the mucus upward towards the laryngopharynx, where it can be swallowed down the esophagus.
Trachea
The trachea (windpipe) extends from the larynx toward the lungs (Figure 12.16a). The trachea is formed by 16 to 20 stacked, C-shaped pieces of hyaline cartilage that are connected by dense connective tissue. The trachealis muscle and elastic connective tissue together form the fibroelastic membrane, a flexible membrane that closes the posterior surface of the trachea, connecting the C-shaped cartilages. The fibroelastic membrane allows the trachea to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation and exhalation, whereas the rings of cartilage provide structural support and prevent the trachea from collapsing. In addition, the trachealis muscle can be contracted to force air through the trachea during exhalation. The trachea is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, which is continuous with the larynx (Figure 12.16b). The esophagus borders the trachea posteriorly.

Bronchial Tree
The trachea branches into the right and left primary bronchi at the carina. These bronchi are also lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium containing mucus-producing goblet cells. The carina is a raised structure that contains specialized nervous tissue that induces violent coughing if a foreign body, such as food, is present. Rings of cartilage, similar to those of the trachea, support the structure of the bronchi and prevent their collapse. The primary bronchi enter the lungs at the hilum, a concave region where blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves also enter the lungs. The bronchi continue to branch into bronchial a tree. A bronchial tree (or respiratory tree) is the collective term used for these multiple-branched bronchi. The main function of the bronchi, like other conducting zone structures, is to provide a passageway for air to move into and out of each lung. In addition, the mucous membrane traps debris and pathogens.
A bronchiole branches from the tertiary bronchi. Bronchioles, which are about 1 mm in diameter, further branch until they become the tiny terminal bronchioles, which lead to the structures of gas exchange. There are more than 1000 terminal bronchioles in each lung. The muscular walls of the bronchioles do not contain cartilage like those of the bronchi. This muscular wall can change the size of the tubing to increase or decrease airflow through the tube.
Respiratory Zone
In contrast to the conducting zone, the respiratory zone includes structures that are directly involved in gas exchange. The respiratory zone begins where the terminal bronchioles join a respiratory bronchiole, the smallest type of bronchiole (Figure 12.17), which then leads to an alveolar duct, opening into a cluster of alveoli.

Alveoli
An alveolar duct is a tube composed of smooth muscle and connective tissue, which opens into a cluster of alveoli. An alveolus is one of the many small, grape-like sacs that are attached to the alveolar ducts.
An alveolar sac is a cluster of many individual alveoli that are responsible for gas exchange. An alveolus is approximately 200 mm in diameter with elastic walls that allow the alveolus to stretch during air intake, which greatly increases the surface area available for gas exchange. Alveoli are connected to their neighbors by alveolar pores, which help maintain equal air pressure throughout the alveoli and lung (Figure 12.18).

The Lungs
A major organ of the respiratory system, each lung houses structures of both the conducting and respiratory zones. The main function of the lungs is to perform the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide with air from the atmosphere. To this end, the lungs exchange respiratory gases across a very large epithelial surface area—about 70 square meters—that is highly permeable to gases.
Gross Anatomy of the Lungs
The lungs are pyramid-shaped, paired organs that are connected to the trachea by the right and left bronchi; on the inferior surface, the lungs are bordered by the diaphragm. The diaphragm is the flat, dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the lungs and thoracic cavity. The lungs are enclosed by the pleurae, which are attached to the mediastinum. The right lung is shorter and wider than the left lung, and the left lung occupies a smaller volume than the right. The cardiac notch is an indentation on the surface of the left lung, and it allows space for the heart (Figure 12.19). The apex of the lung is the superior region, whereas the base is the opposite region near the diaphragm. The costal surface of the lung borders the ribs. The mediastinal surface faces the midline.
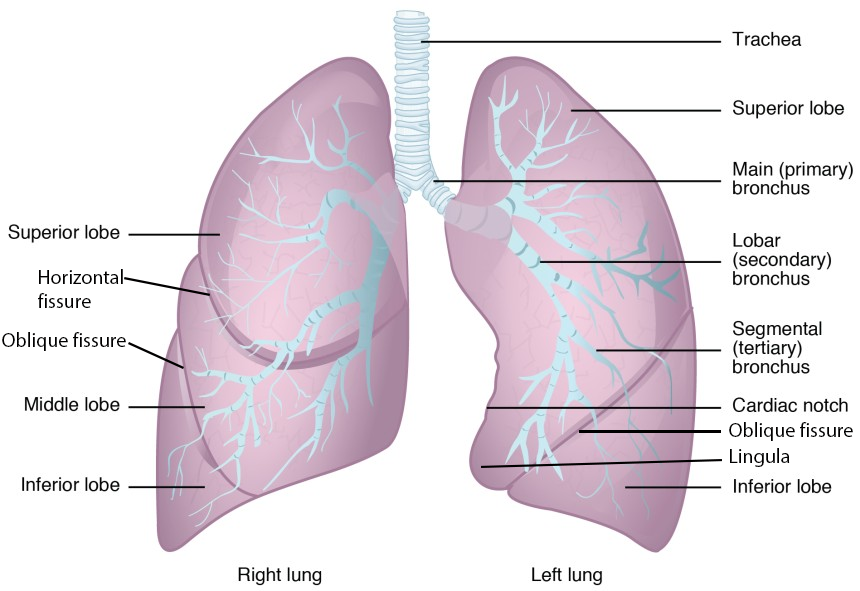
Each lung is composed of smaller units called lobes. Fissures separate these lobes from each other. The right lung consists of three lobes: the superior, middle, and inferior lobes. The left lung consists of two lobes: the superior and inferior lobes. A bronchopulmonary segment is a division of a lobe, and each lobe houses multiple bronchopulmonary segments. Each segment receives air from its own tertiary bronchus and is supplied with blood by its own artery. Some diseases of the lungs typically affect one or more bronchopulmonary segments, and in some cases, the diseased segments can be surgically removed with little influence on neighboring segments. A pulmonary lobule is a subdivision formed as the bronchi branch into bronchioles. Each lobule receives its own large bronchiole that has multiple branches. An interlobular septum is a wall, composed of connective tissue, which separates lobules from one another.
Blood Supply of the Lungs
The blood supply of the lungs plays an important role in gas exchange and serves as a transport system for gases throughout the body. The major function of the lungs is to perform gas exchange, which requires blood from the pulmonary circulation. This blood supply contains deoxygenated blood and travels to the lungs where erythrocytes, also known as red blood cells, pick up oxygen to be transported to tissues throughout the body. The pulmonary artery is an artery that arises from the pulmonary trunk and carries deoxygenated, arterial blood to the alveoli. The pulmonary artery branches multiple times as it follows the bronchi, and each branch becomes progressively smaller in diameter. One arteriole and an accompanying venule supply and drain one pulmonary lobule. As they near the alveoli, the pulmonary arteries become the pulmonary capillary network. The pulmonary capillary network consists of tiny vessels with very thin walls that lack smooth muscle fibers. The capillaries branch and follow the bronchioles and structure of the alveoli. It is at this point that the capillary wall meets the alveolar wall, creating the respiratory membrane. Once the blood is oxygenated, it drains from the alveoli by way of multiple pulmonary veins, which exit the lungs through the hilum.
Pleura of the Lungs
Each lung is enclosed within a cavity that is surrounded by the pleura. The pleura (plural = pleurae) is a serous membrane that surrounds the lung. The right and left pleurae, which enclose the right and left lungs, respectively, are separated by the mediastinum. The pleurae consist of two layers. The visceral pleura is the layer that is superficial to the lungs, and extends into and lines the lung fissures (Figure 12.20). In contrast, the parietal pleura is the outer layer that connects to the thoracic wall, the mediastinum, and the diaphragm. The visceral and parietal pleurae connect to each other at the hilum. The pleural cavity is the space between the visceral and parietal layers.

The pleurae perform two major functions: They produce pleural fluid and create cavities that separate the major organs. Pleural fluid is secreted by mesothelial cells from both pleural layers and acts to lubricate their surfaces. This lubrication reduces friction between the two layers to prevent trauma during breathing, and creates surface tension that helps maintain the position of the lungs against the thoracic wall. This adhesive characteristic of the pleural fluid causes the lungs to enlarge when the thoracic wall expands during ventilation, allowing the lungs to fill with air. The pleurae also create a division between major organs that prevents interference due to the movement of the organs, while preventing the spread of infection.
Unless otherwise indicated, this chapter contains material adapted from chapters 21 and 22 in Anatomy and Physiology (on OpenStax), by Betts, et al. and is used under a a CC BY 4.0 international license. Download and access OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology-2e/

