4.1 Starch and Cereal Introduction
Before You Come to Lab
Name: _________________________________
Read the article posted on Canvas: Classic Smooth and Silky Béchamel (White Sauce) Recipe.
- A white sauce can be used as the base for other sauces or recipes. List three other sauces or recipes from the article.
- What are the three main ingredients in a Bechamel or white sauce (besides salt and pepper)?
- Read through the steps of making a white sauce and list the main steps here (just the bolded part is fine).
Terms, as Used in the Lab Manual
To learn about starch and its functionality, it is helpful to start with definitions.
- Starch Granule: Native structure, energy storage for plant.
- Amylose: Small linear starch molecule, needed to form a gel
- Amylopectin: Large branched starch molecule that contributes a lot of viscosity
- Granule Swelling: First step of gelatinization, water enters the starch granule and starts to swell.
- Gelatinization: Process of starch thickening- absorption of water into granules as starch is heated with liquid.
- Retrogradation: Starch molecules bond together tighter over time, crystalline aggregates in starch gel, further setting of starch gel over storage- lead to syneresis.
- Syneresis: Draining of liquid from gel structure produced by retrogradation.
- Gel vs. Sol: Gel holds its shape, and sol is thickened but still flows.
- Root Starch: Starch extracted from potatoes or cassava (tapioca)
- Cereal Starch: Starch extracted from cereal grains such as corn, wheat, and rice
Corn starch and wheat flour are commonly used starch thickeners. Why might one be used instead of the other?
When making starch-thickened foods, the basic process is heating starch with a liquid while stirring. There are a few added steps to make sure the sauce turns out smooth without lumps. Here are three ways to avoid lumps:
- Mix starch with cold liquid to make a smooth mixture. (Pudding or gravy)
- Mix starch with oil/melted fat to form a smooth paste. (White sauce)
- Mix starch with granular dry ingredients (sugar) to disperse starch granules. (Pudding)
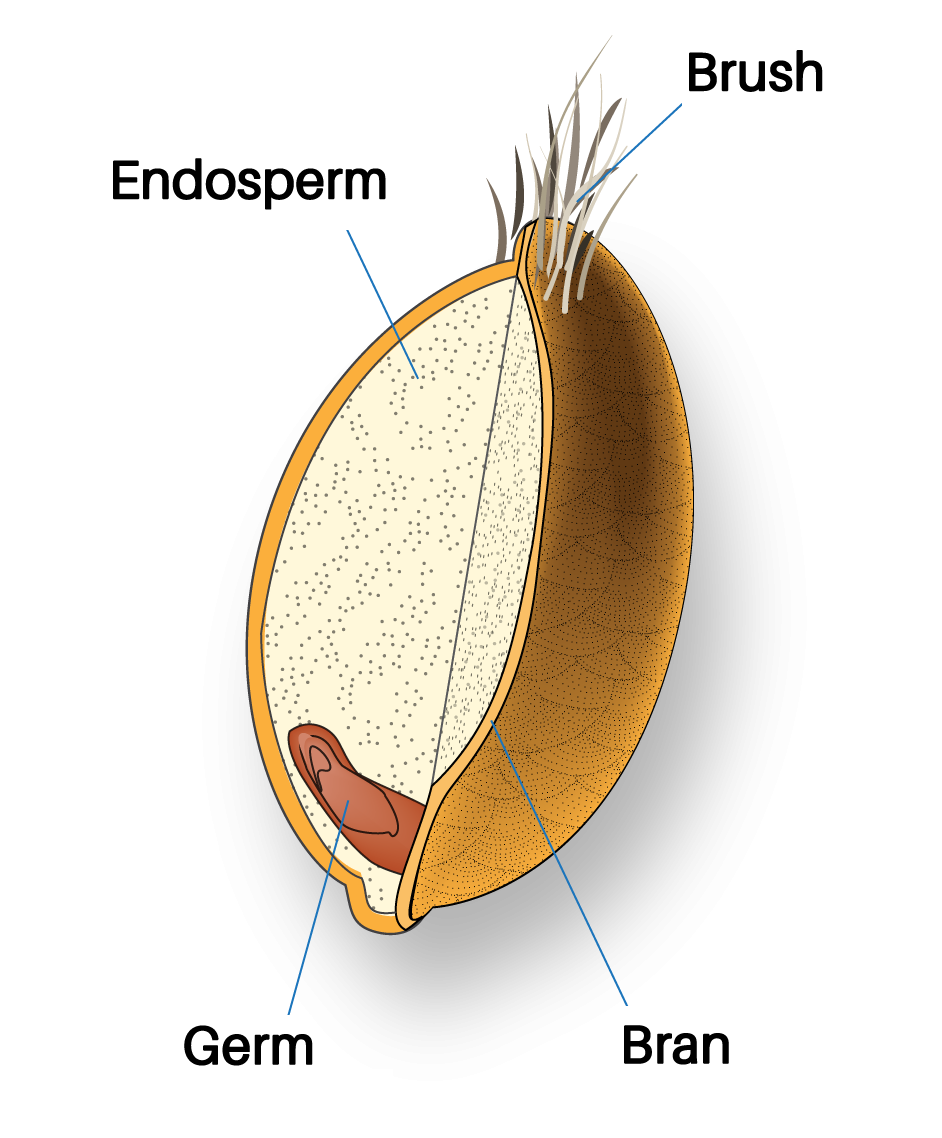
Cereal Grains
Starch comes from a variety of sources, including cereal grains (and root starches, legumes, etc.) Cereal grains fit into two categories: refined grains and whole grains.
Simply put, whole grains include the endosperm, germ, and bran. The Whole Grains Council expands the definition to “Whole grains or foods made from them contain all the essential parts and naturally-occurring nutrients of the entire grain seed in their original proportions.”
Refined grains are endosperm with either the germ, bran, or both the germ and bran removed.

