Infertility
Assisted Reproductive Techniques
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) refer to a group of medical procedures and techniques designed to help individuals or couples achieve pregnancy when traditional methods have not been successful. Several notable assisted reproductive technologies include:
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF is one of the most well-known ART methods. It involves the extraction of eggs from the ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory dish, and then transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus. IVF can be used for various fertility issues, including blocked fallopian tubes, male factor infertility, or unexplained infertility.
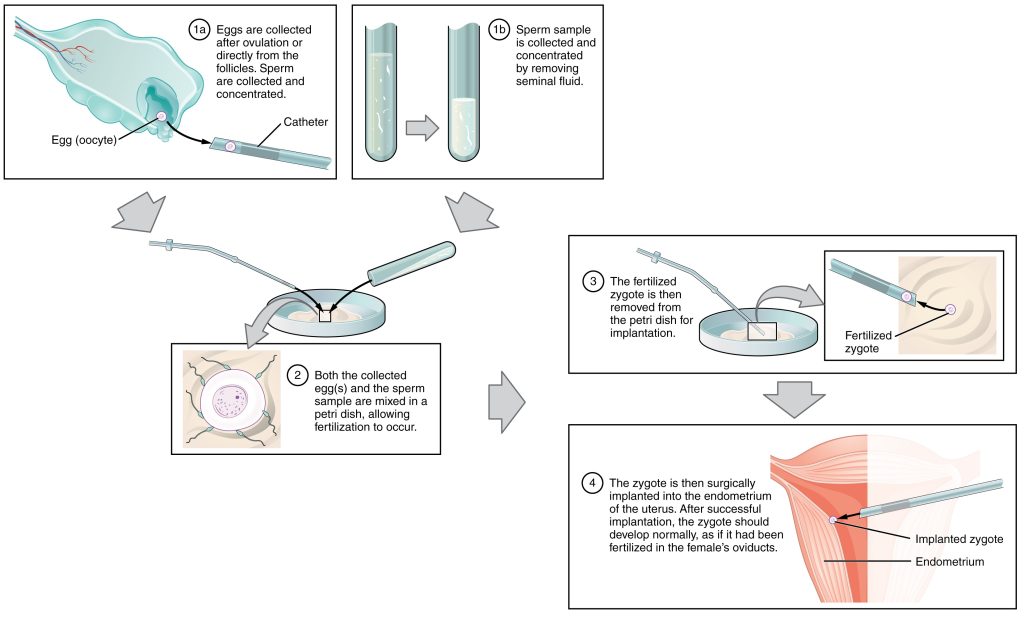
Embryo Cryopreservation
After IVF, excess embryos can be frozen (cryopreserved) for future use, allowing multiple attempts at pregnancy without repeating the ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval process.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
ICSI is a specialized form of IVF where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg to facilitate fertilization. This method is particularly effective in cases of severe male factor infertility or when prior IVF attempts have not been successful.
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT)
GIFT is a technique in which eggs and sperm are collected and placed into the fallopian tubes, allowing fertilization to occur inside the woman’s body. It is less commonly used today due to the popularity of IVF.
Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
ZIFT is similar to GIFT, but it involves the transfer of fertilized embryos (zygotes) into the fallopian tubes. This procedure is also less common than IVF.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
IUI involves placing washed and concentrated sperm directly into the uterus, bypassing the cervix. It is often used for mild male factor infertility or when the cervix is a barrier to conception.
Donor Gametes
Donor sperm or eggs can be used when one partner is unable to provide viable gametes. This is often employed in cases of severe male or female infertility.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
PGT involves testing embryos for genetic abnormalities before transferring them into the uterus. It can help reduce the risk of passing on certain genetic conditions.
Surrogacy
In gestational surrogacy, another woman carries and gives birth to a baby for the intended parents, often using ART to achieve pregnancy. Traditional surrogacy involves the surrogate providing both the egg and carrying the pregnancy.
Assisted reproductive technologies have revolutionized the field of fertility treatment, offering hope to individuals and couples facing infertility. They are complex, highly regulated, and require the expertise of fertility specialists to ensure safe and successful outcomes. However, the cost of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) is very expensive and can vary significantly depending on the specific procedures, geographic location, and individual circumstances.
Image Sources
- Figure. 1. “In vitro fertilization” is from OpenStax Anatomy & Physiology, licensed CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology-2e/pages/1-introduction

