2.3 Effect of pH and Heat on Color and Other Attributes of Fruits and Vegetables; Osmosis; Enzymatic Browning
Objectives
- To identify the major categories of pigments found in fruits, vegetables, and other plant foods.
- To observe the effects of heat and pH of cooking medium on plant pigments.
- To observe the effects of acid or basic cooking medium on the texture of vegetables.
- To observe enzymatic browning.
- To identify some methods of controlling enzymatic browning.
Laboratory Problems
- Identify the major categories of plant pigments.
- Boil vegetables representing each of the pigment categories in water, in acidic solution, and in basic solution.
- Prepare raw fruits in a variety of ways designed to control enzymatic browning.
Terms
- Vegetable Pigments: Chlorophyll, Carotenoids, Anthocyanin, & Anthoxanthin
- Flavor Categories: Mild, Brassica, Allium
- Texture: Cellulose, Pectin, & Hemicellulose
- Enzymatic Browning
- Osmosis
Identify the pigments in each of the vegetables listed below:
Pigment categories: carotenoids, chlorophyll, anthoxanthin, anthocyanin
| Vegetable | Major Pigment | Other Pigment Present |
|---|---|---|
| Red Cabbage | ||
| Cauliflower | ||
| Carrot | ||
| Broccoli |
Prepare assigned vegetable according to specific directions for added ingredients and for covering pan.
Raw vegetable preparation:
- Cabbage (red or green): Remove outer leaves and wash remaining head. It is not necessary to remove the entire core. Shred cabbage into bite-size pieces with a chefs’ knife.
- Cauliflower: Break small flowerets from the head. Wash.
- Carrots: Peel, wash and slice into ¼-inch slices. If the carrot is large, quarter lengthwise before slicing crosswise.
- Broccoli: Cut thin spears about 2 inches long. Wash.
- Onions: Remove outer skin by peeling or by blanching. Cut off root end. Cut onions into bite size pieces. Cook until the flavor is mild.
Lid On and Lid Off Directions:
- Prepare ¼ cup assigned vegetable for each part.
- Boil 1 cup of distilled water for each vegetable. Add vegetable to boiling water; begin timing after water returns to boil.
- Boil until crisp-tender when tested with fork. Record cooking time.
- Reserve a small amount of cooking water for display in custard cup.
- Display vegetable in a custard cup with the sample of cooking water in separate custard cup.
- Record color and texture observations. Do not taste.
Acid/Base Directions:
- Prepare ¼ cup assigned vegetable for each part.
- Boil 1 cup of tap water for each vegetable. Add vegetable to boiling water; begin timing after water returns to boil. Add 1 tsp. vinegar (acid) or ½ tsp. baking soda (base).
- Boil until crisp-tender when tested with fork. Record cooking time.
- Reserve a small amount of cooking water for display in custard cup.
- Display vegetable in a custard cup with the sample of cooking water in separate custard cup.
- Record color and texture observations. Do not taste.
Evaluation
| Major Pigment Vegetable | Lid on | Lid off | Acid
Add 1 tsp vinegar to cooking water |
Base
Add ½ tsp baking soda to cooking water |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthocyanin
|
min | min | min | min |
| Anthoxanthin
|
min | min | min | min |
| Carotenoid
|
min | min | min | min |
| Chlorophyll
|
min | min | min | min |
Observe Osmosis
Objective
- To observe the effect of osmosis on the characteristics of raw fruits and vegetables in storage and in preparation.
Laboratory Problem
- Store fresh raw vegetables in a variety of osmotic conditions.
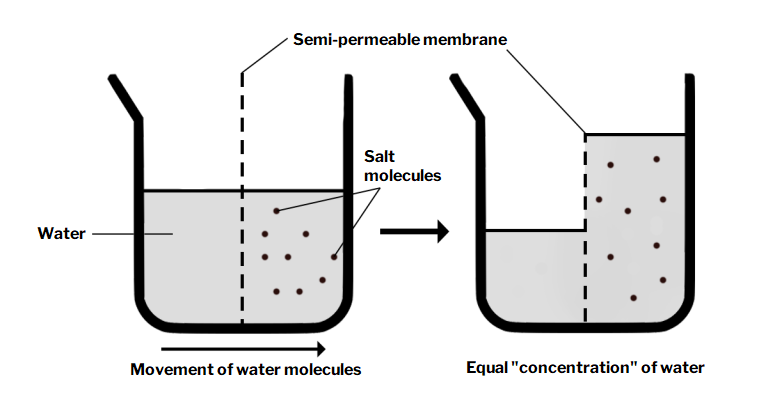
Observe the effect of salt on the appearance and texture of cucumbers:
Cut a small cucumber into 1/8″ slices, divide into three bowls, and treat each sample as directed below. Observe after one hour.
| Method | Appearance | Texture |
| Soak in 1 cup cold water only | ||
| Soak in salt/water solution (2 tbsp salt to 1 cup cold water) | ||
| Sprinkle with 2 tbsp salt only |
Explanation:
Demonstrate enzymatic browning and methods of control:
- With a stainless steel knife, slice an apple or banana onto separate dishes.
- Apply assigned treatment.
- Allow to stand uncovered for one hour.
- Record observations.
| Treatment | Appearance | Flavor |
| None | ||
| Diluted lemon juice (1 part to 3 parts water) | ||
| Commercial anti-darkening agent |
Browning reaction when some fruits and vegetables are cut and exposed to oxygen. Substrate + Enzyme + Oxygen = Browning – OR – Phenolic compounds + Polyphenoloxidase + Oxygen
Water moves across the semi-permeable membrane in response to solute concentration
Partially cook in a large amount of boiling water to inactivate enzymes or to facilitate peeling.

