Potassium
Amber Anderson
- Identify the function of potassium in the plant and potential deficiency symptoms.
- Define the concept of “luxury consumption”
- Identify under what conditions potassium deficiencies might be more likely

Role in the plant
Potassium is contained in the sap rather than structural components of the plant. It is involved in water regulation, such as stomata opening and closing, as well as some enzymatic and energy reactions within the plant. Because of this function, deficiency symptoms may be more evident in hot and dry growing seasons.
Potassium cycle
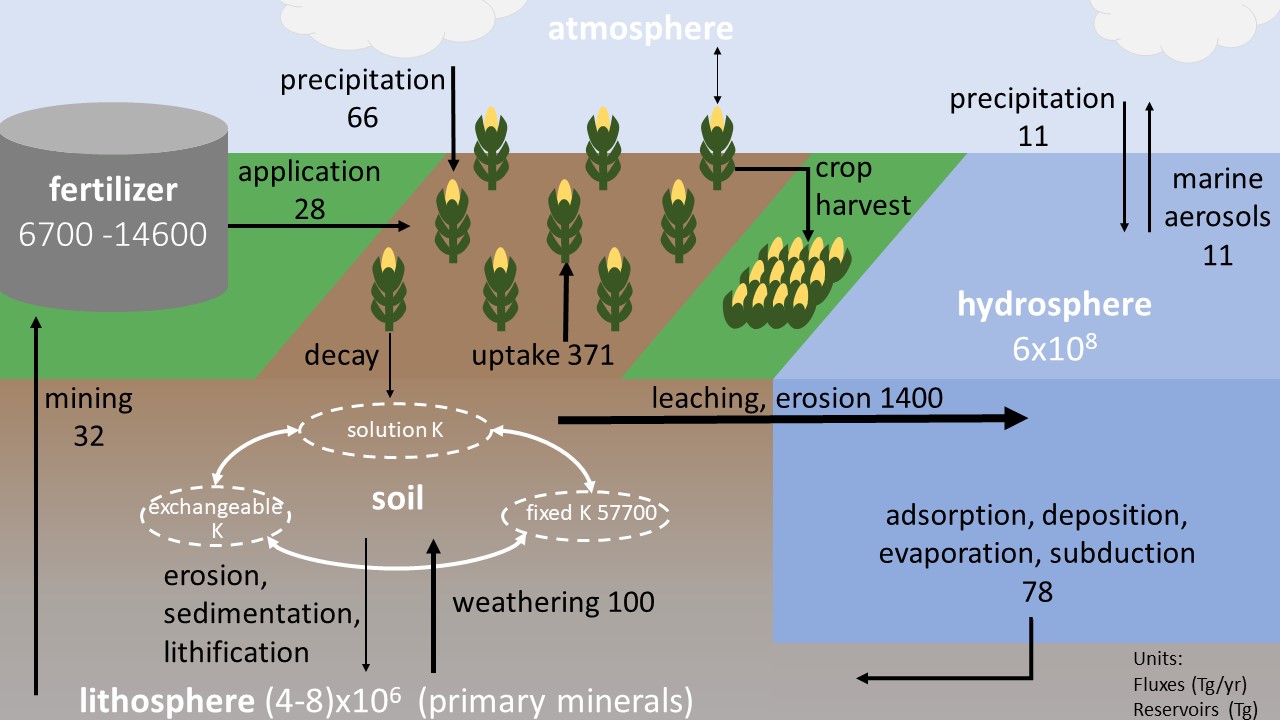
The primary location of potassium in soils are the primary minerals. Small amounts are held on the cation exchange capacity, and significantly less of that is available to the plant in the solution at one time. If the soil can’t supply potassium, fertilizer application would be required. Historically, materials like ‘pot-ash’, or ash from burned materials would be used for potassium enrichment.

Luxury consumption
Luxury consumption is the concept of plant uptake beyond plant needs. If the crop is harvested for grain, this may not be a significant issue. However, if a forage like alfalfa, or silage is produced, this would result in a higher export of potassium from the soil.
Deficiency symptoms
Deficiencies in potassium may be found in areas where the entire plant is removed, while green.
- Potassium is important in water regulation within the plant
- Risk of potassium deficiency increases in areas where plants are harvested green and removed
- Symptoms may be more evident in hot and dry years
- https://www.soils.org/news/science-news/alfalfa-and-potassium-its-complicated/ ↵

